Understanding Radio Frequency Testing: The Key to Wireless System Success
Radio Frequency (RF) testing is the process of measuring and analyzing the electromagnetic waves that are used to transmit signals in a variety of applications, from wireless communication and broadcasting to radar and satellite systems. RF testing involves evaluating the performance, strength, and quality of these signals to ensure they meet specific standards and requirements. This is essential for the development, validation, and maintenance of RF components and systems, as it helps identify any issues that could affect the functionality and reliability of wireless communications and sensing systems. Additionally, RF testing ensures electromagnetic compatibility (EMC)—covering both emissions and immunity to interference—, which are crucial for preventing interference and ensuring that electronic devices can operate harmoniously in their environments.
What is RF Testing?
RF testing is crucial for ensuring the optimal performance and reliability of wireless communication systems and electronic devices. By conducting comprehensive RF tests, engineers can detect and resolve issues related to signal integrity, interference, and overall system efficiency. This not only enhances the quality and functionality of radio components and systems, but also ensures compliance with industry standards and regulatory requirements. Effective RF testing minimizes the risk of costly failures, maximizes operational efficiency, and provides confidence that the wireless technology will perform as expected in real-world conditions. Ultimately, RF testing is critical in developing, certifying, and maintaining devices that rely on radio frequencies, ranging from everyday consumer electronics to specialized industrial equipment, helping companies gain a competitive edge in today’s hyper-connected world.
Frequency (spectrum) vs. Time Domain Analysis
Understanding the differences and similarities between frequency (spectrum) and time domain analysis is crucial for effective Radio Frequency (RF) testing. Each domain offers unique insights and is used to optimize and ensure the proper function of wireless communications within regulated frequency allocations.
Frequency (spectrum) Domain Analysis
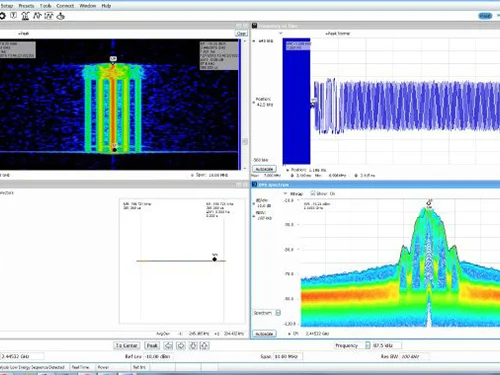
Definition: Frequency (spectrum) analysis is the process of assessing the frequency spectrum of electromagnetic signals to identify and measure their characteristics, such as their amplitude, frequency, and phase. By using a spectrum analyzer, engineers can detect and diagnose issues like signal interference, spurious emissions, and harmonics. Spectrum analysis enables the precise identification of different signal sources within a given bandwidth, ensuring that systems operate efficiently and without unwanted disturbances. It is a fundamental tool in the development, testing, and maintenance of wireless communication systems, broadcasting equipment, radar, and other RF applications.
Use Cases: Spectrum analysis is crucial across multiple industries, including cellular networks and wireless communication, broadcasting, radar and defense, aerospace, medical devices, R&D, compliance testing, and industrial applications because the electromagnetic spectrum is heavily regulated by various organizations like the ITU, FCC, and the EU. It ensures devices comply with these regulations, helps manage the spectrum efficiently, and identifies sources of interference.
Challenges and Solutions: Frequency analysis faces several key challenges, including managing increasingly crowded frequency bands, identifying and mitigating signal interference, and ensuring accurate measurements in complex environments. Engineers must also address the rapid evolution of wireless technologies, which demands continual updates to testing methodologies and equipment. Additionally, maintaining compliance with stringent regulatory standards while optimizing signal performance adds another layer of complexity. These challenges require advanced instruments and software to ensure reliable and efficient RF system operation.
Time Domain Analysis
Definition: Time domain analysis examines how RF signals behave over time, focusing on the changes in phase, amplitude, and frequency. It provides insights into the dynamic characteristics of the signal.
Use Cases: Time-domain analysis of RF signals offers several key advantages, including the ability to capture and analyze transient events and non-repetitive signal behaviors in real time. This method provides detailed insights into signal amplitude, phase, and timing characteristics, enabling precise troubleshooting and optimization of RF systems. Time-domain analysis is particularly effective for identifying issues with fast rising edges, pulsed signals, phase-locked loops, frequency settling, and synchronization problems..
Challenges and Solutions: The primary challenge in the time domain is the accurate characterization of fast-changing signals, critical in advanced communication systems and radar technologies. High-bandwidth, time domain analysis can help overcome this by accurately capturing even small changes in time, and correlating them to signal's behavior in the frequency domain.
Important Tools & Systems for Radio Frequency Testing (RF Testing)
RF Testing is critical for ensuring the performance and efficiency of wireless communication and sensing devices. Here, we focus on the essential tools used in RF testing, which include real-time spectrum analyzers, oscilloscopes, and arbitrary waveform generators, each playing a unique role in the testing process.
Hardware & Systems for Radio Frequency Testing
Real-Time Spectrum Analyzers (RSA)
Key Features:
- High-speed Performance: RSAs are designed for rapid, gapless capture and analysis of high-bandwidth RF signals.
- Real-time Capabilities: Unlike traditional spectrum analyzers, RSAs process signals within their instantaneous bandwidth in real-time, enabling them to capture transient events that other instruments may miss. They empower thorough analysis of complex communication and radar signals.
Applications: RSAs are indispensable in environments where speed and accuracy are critical, such as in testing dynamic wireless signals and complex interference scenarios.
Typical Locations for Use:
- Laboratory Settings: RSAs are commonly used in R&D labs for developing new components and systems for wireless technologies, where real-time analysis is crucial for detecting fast-moving anomalies and spurious signals.
- Manufacturing Facilities (Fab): In manufacturing test, RSAs ensure that products meet the required RF and emissions specifications, and can help calibrate their RF power before they reach the end user.
- Field Testing: Engineers use portable RSAs for onsite diagnostics, troubleshooting, and field system validation, especially in radar, telecommunications and broadcasting.
Oscilloscopes
Key Features:
- Versatile Bandwidth Options: Ranging from a few MHz to several GHz of instantaneous bandwidth.
- Multi-channel Models: Available in both 2, 4, and up to 8 channel configurations, enhancing the ability to monitor multiple signals simultaneously.
Applications: Oscilloscopes are crucial for detailed analysis of the time-domain characteristics of electronic signals, particularly useful in research and development settings for debugging and signal integrity checks.
Typical Locations for Use:
- Laboratory Settings: Essential for research, development, and validation of the timing behavior of electronic signals.
- Manufacturing Facilities (Fab): Used to ensure that electronic designs and systems meet tight timing standards during production.
- Field Testing: Portable models are employed to diagnose and troubleshoot issues in real-world operational environments, such as communication infrastructure sites.
Arbitrary Waveform Generators (AWG)
Key Features:
- Flexibility: AWGs offer unmatched capabilities to generate any waveform, tailored to specific test conditions, either as a single occurrence or a repetitive signal.
Applications: AWGs are particularly valuable in simulating complex waveforms and testing device responses under varied signal conditions, aiding in the development of robust and efficient wireless devices.
Typical Locations for Use:
- Laboratory Settings: Widely used in the design and testing phases to simulate and analyze different signal scenarios.
- Manufacturing Facilities (Fab): Critical in validating final product functionalities and stress testing under realistic conditions.
- Field Testing: Useful for on-site generation of specific signals required to test system responses in a real-world setting.
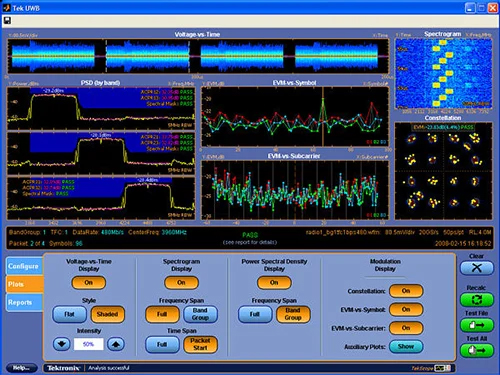
RF Testing Software Overview
Software plays a crucial role in RF testing, enhancing the functionality of hardware through advanced signal processing, analysis, and simulation capabilities.
Key Features:
- Signal Analysis: Software tools provide extensive analysis results, helping engineers understand spectrum utilization, signal modulation quality, system stability, and performance.
- Simulation Capabilities: RF testing software can simulate complex wireless environments and signal interactions, allowing engineers to predict how devices will perform in real-world scenarios.
- Automated Testing: Many RF testing software packages include automation features, which streamline the testing process, reduce human error, and increase repeatability and efficiency.
- Data Management: Effective software helps in organizing, storing, and retrieving test data, enabling easier reporting and compliance tracking.
Applications:
- Design Validation: Software is used extensively in the design phase to characterize all the key RF parameters of a radio system, validate its use cases, and ensure the electromagnetic compatibility and signal integrity of radio devices.
- Regulatory Compliance: Ensures that all wireless devices meet global communication standards and regulations through meticulous calibration and testing procedures.
- Performance Optimization: Helps in tuning devices for optimal RF performance in various conditions by providing detailed feedback on device behavior under different operating parameters.
Accessories and Adapters for RF Testing
Accessories and adapters are indispensable in extending the capabilities of RF testing equipment, ensuring accurate and efficient measurement and analysis.
Key Features:
- Cables and Connectors: High-quality cables and connectors are essential for maintaining signal integrity during tests. They must match the impedance of the system to avoid reflection and loss.
- Signal Attenuators: These are used to reduce the power of a signal without significantly distorting its waveform. Attenuators are crucial for protecting sensitive equipment from high signal levels.
- Antennas: Different tests may require various types of antennas to accurately capture or emit signals. Antennas must be chosen based on the specific frequency and radiation pattern required for the test.
- Adapters: These help in interfacing different types of connectors and cables, ensuring compatibility between various pieces of testing equipment.
- Calibration Kits: Regular calibration using appropriate calibration kits is necessary to ensure that RF testing equipment provides accurate and consistent results.
Applications:
- Extended Testing Range: Accessories like high-gain antennas and broadband cables allow testing across a broader range of conditions and setups.
- Signal Characterization: Using the correct adapters and cables ensures that the signal is not altered during testing, leading to more accurate characterization.
- Device Compatibility: Adapters and calibration kits help in maintaining the versatility of testing equipment, making them compatible with a wide range of devices and standards.

 KALİBRASYON LABORATUVARI
KALİBRASYON LABORATUVARI